Beyond the Buzz: How Americans are planning for a sober future
We are entering an era where many consumers are re-evaluating their relationship with alcohol. According to the Ipsos Consumer Tracker, 40% of Americans resolved to reduce alcohol consumption in 2025, marking a 4% increase from the previous year. The Ipsos Alcohol Consumption Tracker (ACT) highlights this behavioral shift, compelling the alcoholic beverage industry to adapt by creating low-to-no-alcoholic beverages to continue to retain portfolio market share.
To understand the motivations behind this shift, the Ipsos Behavioral Science team developed the Ipsos ALC Framework to help brands address drivers of reduced alcohol consumption. This framework is based on Self-Determination Theory, which posits that intrinsic motivation arises when a behavior is perceived as worthwhile, controllable, and socially connected.
Consequently, the ALC framework consists of three pillars focusing on intrinsic motivation to reduce alcohol consumption:
- Attitudes: Focuses on individuals' health knowledge and attitudes toward alcohol and alcohol substitutes
- Locus of Control: Focuses on a person's perceived control over their drinking habits and decisions
- Connectedness: Focuses on the robust relationship between social relationships and drinking behaviors
Attitudes
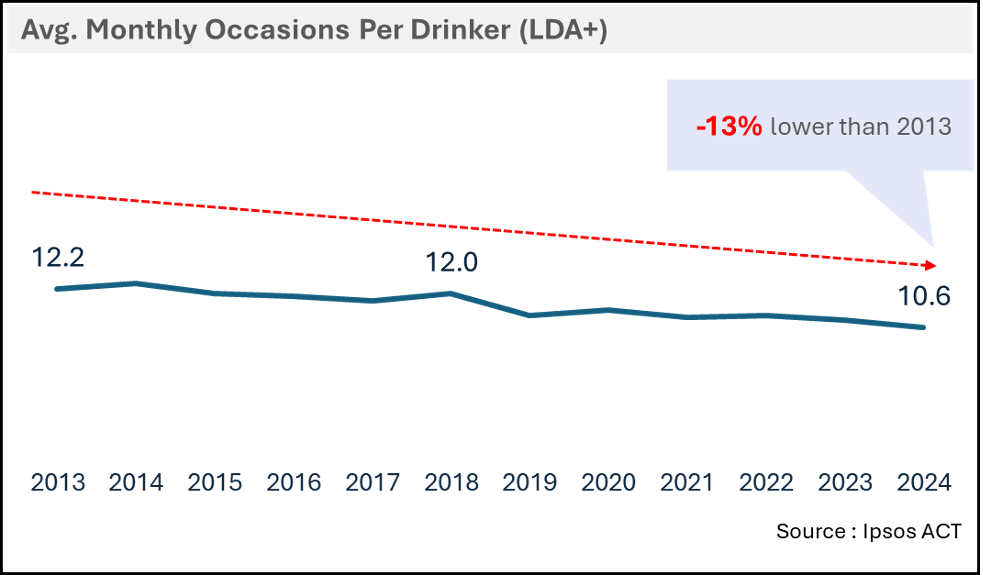
Previously, moderate alcohol consumption was believed to be beneficial (e.g., “red wine is good for the heart”). However, today, there are increasing questions about the impact of alcohol on health. Over a third of legal drinking age individuals in ACT express concern about alcohol's health effects, and half report reducing their intake in 2024. The emphasis on health and wellness in the media has underscored the negative impact of alcohol — even in moderation. Non-alcoholic beverages are gaining popularity, with nearly 35% of ACT respondents also consuming non-alcoholic options. Brands should capitalize on this trend by promoting low-to-no alcohol beverages that align with consumer health goals.
Considerations for your business:
✔ Do you know if your consumer base is taking active steps to stay healthy?
✔ Are you aware of specific occasions where health is prioritized over alcohol consumption? Are you poised to win there?
✔ Have you considered the impact of GLP-1 usage on your business?
Locus of Control
The rise of alcohol substitutes has provided consumers with more choices, allowing them to redefine their drinking habits. The Sober Curious movement marks a departure from older norms: In 2024, two in five ACT drinkers set intentional limits on their alcohol intake, and half of 18- to 34-year-olds resolved to drink less in 2025, compared to one in four Americans over 55. When drinking at bars or parties was the norm, abstaining was often seen as breaking the norm. However, the Sober Curious movement and the availability of low-to-no alcohol options at social events have created a new norm where consumers feel empowered to decide whether to drink.

Considerations for your business:
✔ Do you understand your current consumers' beverage repertoire and alternative options?
✔ Does your portfolio cater to the Sober Curious?
✔ Have you developed a strategy to communicate, engage and win with the Sober Curious effectively?
Connectedness
Consumers tend to invest in relationships with like-minded people, often mirroring their behaviors. The motivation to reduce alcohol consumption is linked to social interactions and where these interactions occur. Peer groups typically influence drinking habits; when a group reduces alcohol intake, individuals often follow suit to fit in or gain acceptance. This shift may lead to shared interests in low-to-no alcohol beverages. While alcohol is often viewed as a social lubricant, data suggests younger generations are less likely to frequent bars and clubs compared to older generations. This change may reduce the perceived need for alcohol as an aid to socialization, motivating individuals to choose low-to-no-alcohol options. As social dynamics evolve, mindful and moderate drinking practices are becoming more prevalent.

Considerations for your business:
✔ Are you clear on the emotional and functional benefits consumers seek from your brand?
✔ What information sources do your consumers use to explore new offerings?
✔ Are you aware of how the on and off premise social occasions of consumption are evolving?
Understanding consumers’ intrinsic motivation is crucial to uncovering the unconscious drivers of alcohol consumption. The ALC framework can help brands develop a brand, innovation and communications strategy that aligns to consumer goals. As a leader in market research and behavioral science, Ipsos leverages syndicated data and beverage industry expertise to deliver effective solutions to help brands succeed in this evolving landscape.
- Learn more about the Ipsos Alcohol Consumption Tracker
- Learn more about Ipsos’ Behavioral Science Approach: Contact Jesse Itzkowitz at [email protected], Eliana Polimeni at [email protected], or James Moran at [email protected]
- Learn more about the Brand Success Framework


