Ipsos Encyclopedia - Product Testing
Product Testing, also called consumer testing or comparative testing, is the process of measuring the properties or performance of products. Product testing is any means by which a researcher measures a product's performance, safety, quality, and compliance with established standards. The primary objective is to conduct a test among consumers independently of the manufacturers, suppliers, and marketers of the products.
Product Testing seeks to ensure that consumers can understand what products will do for them and which products have the best values. It enables manufacturers to increase consumer protection by checking that the claims made during marketing activities such as advertising and promotions are met.
Product Testing might be executed by a supplier such as Ipsos, a manufacturer, an independent laboratory, a government agency, etc. Often an existing formal test method is used as a basis for testing. Other times engineers develop methods of test which are suited to the specific purpose.
There are variety of purposes for Product Testing, such as:
- Decide if a new product development program is on track: Demonstrate proof of concept
- Provide standard data for other R&D, engineering, and quality assurance functions
- Provide a technical means of comparison of several options
- Provide evidence in legal proceedings: product liability, product claims, etc.
- Help solve problems with current product
- Help identify potential cost savings in products
Product tests can be used for:
- Subjecting products to stresses and dynamics expected in use
- Reproducing the types of damage to products found from consumer usage
- Controlling the uniformity of production of products or components
Ipsos Point of View
A product is at the core of any marketing mix model and the physical manifestation of a brand promise. Awareness and marketing effectiveness will generate trial, but the product performance in meeting consumer needs, being memorable and offering the right value are critical for repeat purchasing.
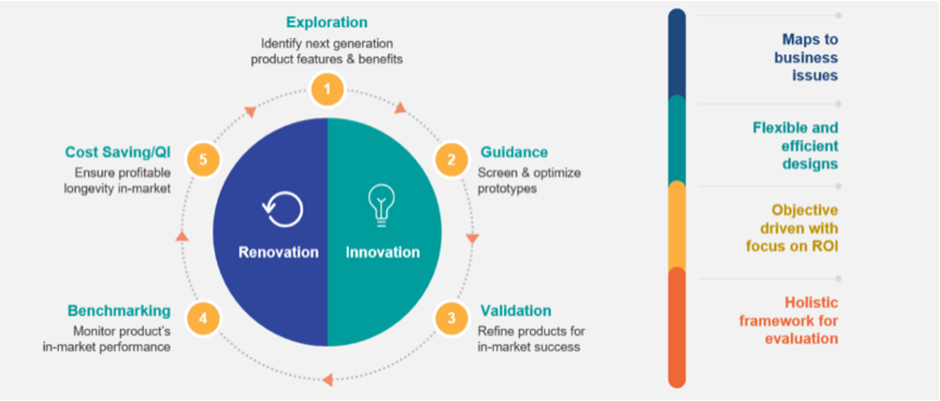
Product Testing is relevant for the whole product lifecycle. The Lifecycle covers multiple stages (see Figure 1), all of which must be supported to identify new opportunities and to extend the life of the product.
As the world’s largest product testing adviser, Ipsos provides a suite of solutions grounded in Real Insights from Real People for sensory optimization, category appraisals, prototype screening, concept/product fit, competitive benchmarking, cost savings and product quality improvements, i.e. across the whole product lifecycle. Our suite of solutions is valid to the ever-changing market dynamics.
Product Testing in today’s world needs to be agile and cost efficient while providing the required rigor for a proper and successful product innovation or renovation. Using unique, award-winning proprietary solutions we help clients to create superior products. Our aim is to continuously improve the way we test at the different stages of the product lifecycle.
There are three important things you should remember about Product Testing at Ipsos:
- We are big and innovative. We are the LARGEST PRODUCT TESTING ORGANIZATION in the world, and have won many awards on innovating product research
- We partner across all stages of product development and work with different client departments: CMI, Marketing, CTI, and Digital Teams
- We are experienced in developing client-based protocols and deploying global programs. We provide rigor in our data collection and have analyses that provide clear directions and next steps.
Have you seen?
Ipsos KEYS – Great Expectations https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DmttxcN20Mw
Further Reading
We’re More than Our Senses: Taking product development to the next level:
https://www.ipsos.com/en/were-more-our-senses-taking-product-development-next-level
Adapting Product Testing in Challenging Times:
https://www.ipsos.com/sites/default/files/ct/publication/documents/2020-07/adapting-product-testing-ipsos.pdf

![[Webinar] Global Voices of Experience 2026 - Ipsos](/sites/default/files/styles/list_item_image/public/ct/event/2026-02/global-voices-of-experience-carousel.webp?itok=BEAGdhsC)

