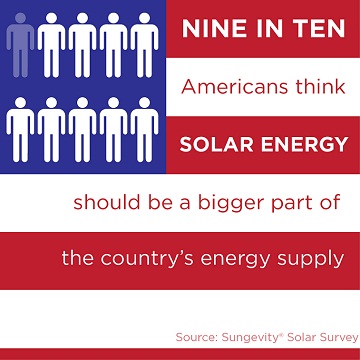
Nine in Ten Adults Agree that Solar Energy Should Be a Bigger Part of America's Energy Supply in the Future
- Women are more likely than men to say that solar energy should be a bigger part of America's energy supply (91% vs. 86%), and that jobs created in the solar energy sector are better for the economy and the environment than in traditional fossil fuel industries (77% vs. 67%).
Three quarters (74%) of adults also agree that increased use of solar power will stimulate our economy by creating good-paying jobs at home. Additionally, nearly two thirds (64%) agree that the solar energy industry is creating long term American jobs that won't be outsourced in the future, more so than the manufacturing industry.
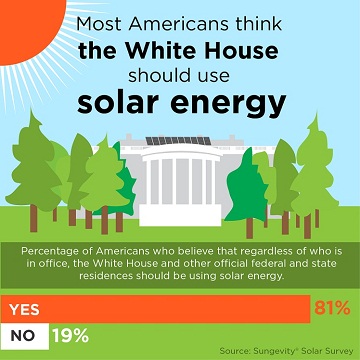
As many see economic advantages to increased use of solar power, 80% expect their elected officials to support solar energy initiatives. In fact, a similar proportion (81%) believe that regardless of who is in office, the White House and other official federal and state residences should be using solar energy.
Financial rather than Environmental Benefits Are the Top Motivator for Supporting Solar Energy
With four in five believing that the increased use of solar power will reduce household's energy costs (82%), it is no surprise that U.S. adults recognize the financial benefits of using solar energy. Eight in ten (79%) adults agree that biggest benefits that would encourage support for solar energy are financial in nature, such as reduced energy costs (60%), decreased dependence on the fluctuating cost of fossil fuels (26%), federal/state tax credits (21%) and increased home value (12%).
- Women (65%) are among those most likely to believe that reduced energy costs are one of the biggest benefits. Parents are also more likely than those without young children to say that federal and state tax credits are one of the main benefits that would encourage support for solar energy (26% vs. 20%).
- Residents of the South (28%) are more likely than those living in the Northeast (20%) report that a top benefit would be the decreased dependence on the fluctuating cost of fossil fuels.
Fewer, 59%, select environmental benefits as top reasons for supporting solar energy, such as being better for the environment and reducing emissions (44%) and increased energy independence (28%).
- Women are more likely than are men to say that reducing emissions is one of the biggest benefits that would encourage them to support solar energy (49% vs. 40%).
Cost Is the Main Barrier to Using Solar Energy
While many see the financial benefits of using solar energy, costs are also the greatest obstacle. Eight in ten (80%) adults state that the biggest barriers to using solar energy are financial related concerns, including set up cost such as installation (72%) and difficult and costly maintenance (43%). Similarly, nearly nine in ten (87%) adults believe that the costs of incorporating and installing renewable sources of energy into homes need to decrease in order for them to be more widely used.
- Residents in the Midwest (89%) and South (89%) are also more likely than those in the West (80%) to believe that set-up costs need to go down in order for solar energy to be more widely adopted.
Adults are also apprehensive to use solar energy due to the stress in dealing with technical installation such as updating electrical systems and zoning laws etc. (47%). Other reasons for not using solar energy is the belief that it may not be available in the area (16%), it wouldn't generate enough energy (19%), they may not live in a sunny location (12%) or they just dislike the look of solar panels (10%).
- Residents of the Midwest (15%) and Northeast (17%) are more likely to worry about the amount of sun exposure than are those living in the South (8%). A greater proportion of those living in the Midwest also express concern about how much energy solar panels could produce (25%).
Powering their Homes
While seven in ten adults (70%) mention that they reviewed their energy bills in the past month, 6% have not done so in the last six months, and 7% report that they have never reviewed their energy bill. While a majority of adults (59%) have considered how the electricity in their house is generated, 41% have not.
- Men are more likely to say they have thought about the source of the energy that powers their home than are women (68% vs. 51%).
Over three quarters of adults (77%) wish they could take advantage of renewable energy sources like solar energy to power their home. In fact, over half (53%) have considered incorporating renewable energy such as solar as a way of powering their home. Residents in the South (56%) and in the West (59%) are more likely have considered using solar energy than those in the Midwest (44%).
However, many are lacking information about solar energy options, with 70% wishing they knew more about renewable energy sources like solar energy. Additionally, nearly half (48%) are confused about solar energy options, with women being more likely to be confused than men (52% vs. 44%).
Just 41% of adults believe that the sun generates enough energy to power their home, and they are even less confident about larger areas such as their neighborhood (33%), their town or city (29%), and their state (25%). However, 39% believe that the sun generates enough energy to power the entire county, with men being more likely than women to believe so (42% vs. 35%). Three in ten (29%) were not sure about what the sun would be able to power.
When it comes to powering different parts of their own home, some confusion persists. While roughly three quarters believe that solar energy can be used for lighting the house (77%), heating the house (75%), heating the water (74%), and powering appliances (71%), fewer (64%) think that solar energy can also cool their house. One in eight (12%) were not sure about what solar energy would be able to power, and 1% doesn't believe that solar energy could be used for any of these purposes.
- Men are more likely than are women to understand that solar energy can heat water (78% vs. 70%) and power appliances (75% vs. 67%).
These are some of the findings of an Ipsos poll conducted September 13-17, 2012. For the survey, a national sample of 1,006 adults from Ipsos' U.S. online panel were interviewed online. Weighting was employed to balance demographics and ensure that the sample's composition reflects that of the universe. A survey with an unweighted probability sample of this size and a 100 percent response rate would have an estimated margin of error of +/- 3 percentage points 19 times out of 20 of what the results would have been if the entire population of adults aged 18 and older in the United States had been polled. All sample surveys and polls may be subject to other sources of error, including, but not limited to coverage error, and measurement error.
For more information on this news release please contact:
Rebecca Sizelove Senior Research Manager Ipsos Public Affairs 212.584.9253 [email protected]
About Ipsos Public Affairs
Ipsos Public Affairs is a non-partisan, objective, survey-based research practice made up of seasoned professionals. We conduct strategic research initiatives for a diverse number of American and international organizations, based not only on public opinion research, but elite stakeholder, corporate, and media opinion research.
Ipsos has media partnerships with the most prestigious news organizations around the world. In the U.S., UK and internationally, Ipsos Public Affairs is the media polling supplier to Reuters News, the world's leading source of intelligent information for businesses and professionals, and the Hispanic polling partner of Telemundo Communications Group, a division of NBC Universal providing Spanish-language content to U.S. Hispanics and audiences around the world.
Ipsos Public Affairs is a member of the Ipsos Group, a leading global survey-based market research company. We provide boutique-style customer service and work closely with our clients, while also undertaking global research.
To learn more visit: www.ipsos-na.com
About Ipsos
Ipsos is an independent market research company controlled and managed by research professionals. Founded in France in 1975, Ipsos has grown into a worldwide research group with a strong presence in all key markets. In October 2011 Ipsos completed the acquisition of Synovate. The combination forms the world's third largest market research company.
With offices in 84 countries, Ipsos delivers insightful expertise across six research specializations: advertising, customer loyalty, marketing, media, public affairs research, and survey management.
Ipsos researchers assess market potential and interpret market trends. They develop and build brands. They help clients build long-term relationships with their customers. They test advertising and study audience responses to various media and they measure public opinion around the globe.
Ipsos has been listed on the Paris Stock Exchange since 1999 and generated global revenues of e1,363 billion (1.897 billion USD) in 2011.
Visit www.ipsos-na.com to learn more about Ipsos offerings and capabilities.